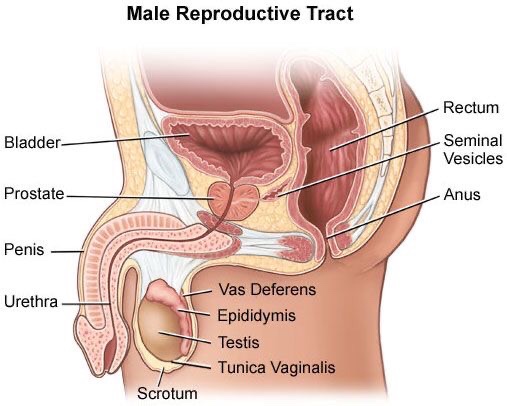
The prostate is a small gland located in the male reproductive system situated below the bladder and in front of the rectum.
The main function of the prostate is to produce fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. As men age, the prostate can sometimes develop health issues, such as enlargement (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or in some cases, cancer.
Doctor who specializes in Prostate cases:
A urologist is the type of doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of conditions related to the male reproductive system, including the prostate. They are often the primary healthcare professionals responsible for managing prostate health and addressing issues such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and prostate cancer.
It’s important for men to be aware of potential signs or symptoms that might indicate a need to get checked for prostate issues.
These can include:
Frequent Urination: If you find yourself needing to urinate more often than usual, especially at night, it could be a sign of a prostate issue.
Firm Partners Federal Government In Promoting Proper Hygiene Sensitizing
Difficulty Starting or Stopping Urination: Struggling to begin or end urination, or experiencing weak urine flow, might be indicative of a prostate problem.
Pain or Discomfort: Any pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, lower back, or hips should be evaluated, as it could be related to the prostate.
Blood in Urine or Semen: The presence of blood in urine (hematuria) or semen (hematospermia) should be promptly addressed.
Erectile Dysfunction: While this can have various causes, it may be linked to prostate health issues.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Levels: Elevated PSA levels in a blood test can be an indicator of prostate problems, although it’s important to note that a high PSA level doesn’t necessarily mean cancer.
Change in Sexual Function: This can include problems with ejaculation, pain during ejaculation, or decreased sexual desire.
Frequent Pain or Stiffness in the Lower Back, Hips, or Upper Thighs: This might be associated with an advanced stage of prostate cancer.
Unexplained Weight Loss or Fatigue: These can be general signs of health issues, including potential prostate problems.
Difficulty Controlling Urination (Incontinence): If you’re experiencing urine leakage or difficulty controlling your bladder, it’s important to seek medical attention.
There are several potential triggers or risk factors that can contribute to prostate health issues.
These include:
Age: Prostate issues, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer, become more common as men get older.
Family History: A family history of prostate problems, especially prostate cancer, can increase the risk.
Ethnicity: Prostate cancer is more prevalent in certain ethnic groups, particularly African American men.
Diet and Lifestyle: High-fat diets, obesity, and sedentary lifestyles have been associated with an increased risk of prostate issues.
Hormonal Factors: Imbalances in hormones like testosterone and estrogen can affect prostate health.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals or toxins may be linked to prostate problems, although the specific culprits are not always clear.
Sexual Health: There might be a connection between sexual activity, number of partners, and the risk of prostate issues, although the exact nature of this link is still being researched.
Medical History: Previous medical conditions, such as sexually transmitted infections or inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis), may increase the risk of future prostate issues.
Medications: Some medications or supplements might affect prostate health. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider about any potential side effects.
Prostate screening typically involves a combination of two main tests:
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): This is a physical examination in which a healthcare provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel the prostate for any abnormalities in size, shape, or texture.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: This is a blood test that measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels can indicate various prostate conditions, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer.
Can I test for prostate at home?
There isn’t a widely available home test for prostate cancer or other prostate issues that is considered as reliable as professional medical testing.
The management of prostate health depends on the specific issue. Here are some common approaches for different prostate conditions:
1. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH):
Lifestyle Changes: This can include dietary adjustments (such as reducing caffeine and alcohol intake), regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Medications: Certain medications can help alleviate symptoms of BPH. These may include alpha-blockers, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, or combination therapies.
Minimally Invasive Procedures: In more severe cases, procedures like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or laser therapy might be recommended.
Surgery: In severe cases or when other treatments have failed, surgery to remove part or all of the prostate may be necessary.
2. Prostate Cancer:
Active Surveillance: For low-risk cases, doctors may choose to monitor the cancer rather than immediately treat it.
Surgery (Prostatectomy): This involves removing the prostate gland and is a common treatment for localized prostate cancer.
Radiation Therapy: This can be done using external beams or internal radiation sources (brachytherapy) to kill cancer cells.
Hormone Therapy: This aims to reduce the level of testosterone, which can slow the growth of prostate cancer cells.
Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy: These may be used for more advanced cases.
3. Prostatitis:
Antibiotics: If the prostatitis is bacterial in nature, antibiotics will be prescribed.Pain Management:
Medications for pain and inflammation may be recommended.
Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding irritants like caffeine and alcohol, as well as regular exercise, can be beneficial.
4. Prostate Health Maintenance:
Regular Check-ups: Routine visits to a healthcare provider for prostate screenings and overall health assessments.
Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can support prostate health.
In Conclusion
Consult a Healthcare Professional: The first step is to schedule an appointment with a urologist or primary care physician. They can assess the situation, perform necessary tests, and provide personalized advice.
Open Communication: Be candid with your healthcare provider about your fears, symptoms, and any family history of prostate issues. This information helps them make informed decisions.
Regular Check-ups: Routine check-ups are crucial for monitoring prostate health. Early detection of any issues can lead to more effective treatments.
Stay Informed: Educate yourself about prostate health, including common conditions like BPH and prostate cancer. Knowing what to expect can help alleviate fears.
Don’t Delay Seeking Help: If you experience symptoms like frequent urination, difficulty urinating, or pain, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider.
Early intervention is crucial.Remember, this advice is general in nature and not a substitute for personalized medical guidance. Always consult a healthcare professional for specific concerns about prostate health.




One thought on “The A- Z Knowledgeable Factors Of Prostate”